Create Azure Web App Action
This action is a wrapper for the Azure command line: az webapp create. If you're having trouble using this action, or any of the Azure actions, please refer to the Azure command line reference.
The Create Azure Web App action is a premium action that can be used to create web apps on Azure.
Before creating an Azure Web App, you will need a Resource Group and an App Service Plan. See also the Delete Azure Web App Action.
Create Azure Web App
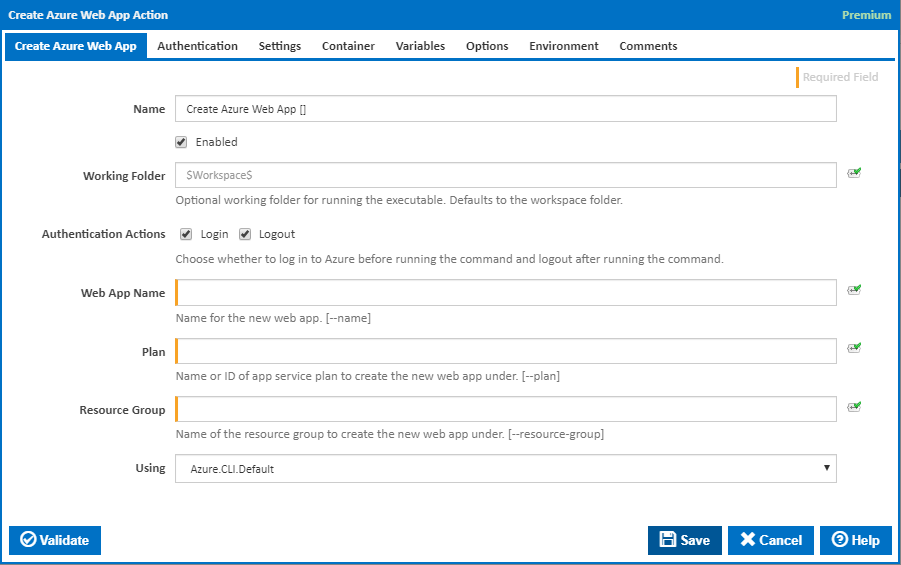
Name
A friendly name for this action (will be displayed in the actions workflow area).
Enabled
Determines if this action will be run within the relevant stage.
Working Folder
The folder where the command line executable is run. This is optional and defaults to the workspace folder.
Authentication Actions
Generally you will need to log in to Azure before running this action and log out afterwards. If you have several Azure actions in a stage, you can avoid repeated logins by unchecking the Login action on all but the first Azure action and unchecking the Logout action on all but the last Azure action. The Authentication tab will be shown if either of these options is ticked.
Web App Name
The name of the new web app. This can include alphanumeric characters and hyphens but no spaces. [---name]
Plan
The name or ID of an existing app service plan to create the new web app under. [---plan]
Resource Group
The name of an existing resource group to create the new web app is under. [---resource-group]
Using
The version of the Azure command line to use. It is important that the agent has the correct version of the Azure command line installed for command provided.
The Using drop down is populated with any property collector whose namespace matches the pattern defined by the Create Azure Resource Group action. The pattern for this action is ^Azure.Cli.*
If you create a property collector for this action, make sure you select the Path Finder PlugIn type and give it a name that will match the pattern above in blue. Example names listed here, search the table's Plugin column for "Azure Command".
For more in-depth explanations on property collectors see Property Collectors.
Alternatively, you can select the Custom option from the Using drop down list and specify a path in the resulting input field that will be displayed. Please read Why it's a good idea to use a property collector before using this option.
Authentication
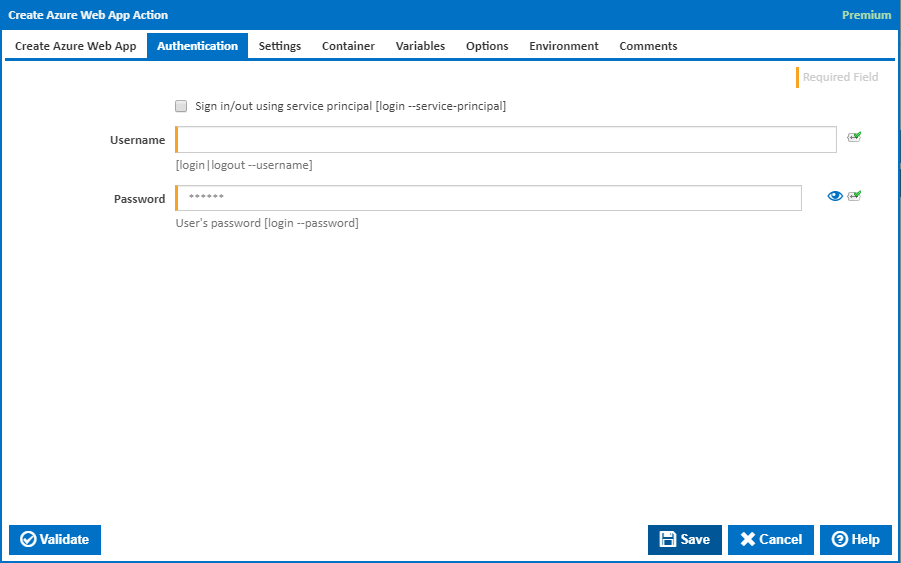
Sign in/out using service principal
Tick this to log in or out using a service principal instead of a username and password. An Azure service principal is an identity created for use with applications, hosted services, and automated tools to access Azure resources. This access is restricted by the roles assigned to the service principal, giving you control over which resources can be accessed and at which level. For security reasons, it's always recommended to use service principals with automated tools rather than allowing them to log in with a user identity. [login --service-principal]
Username
Enter a username to log into the Azure cloud. This is generally an email address. [login|logout --username]
Password
The password associated with the Azure username. [login --username]

Name or URL
Enter the application name or URL associated with the service principal. [login --service-principal --username]
Client Secret or Certificate
Enter the service principal password, or the path to a X509 certificate used to create the service principal in PEM format. [login --service-principal --password]
Tenant
Enter the tenant associated with the service principal, as either an .onmicrosoft.com domain or Azure object ID. [login --service-principal --tenant]
Use certificate SN issuer
Tick to support automatic certificate rollovers with service principals configured with Subject Name and Issuer Authentication. [login --use-cert-sn-issuer]
Settings
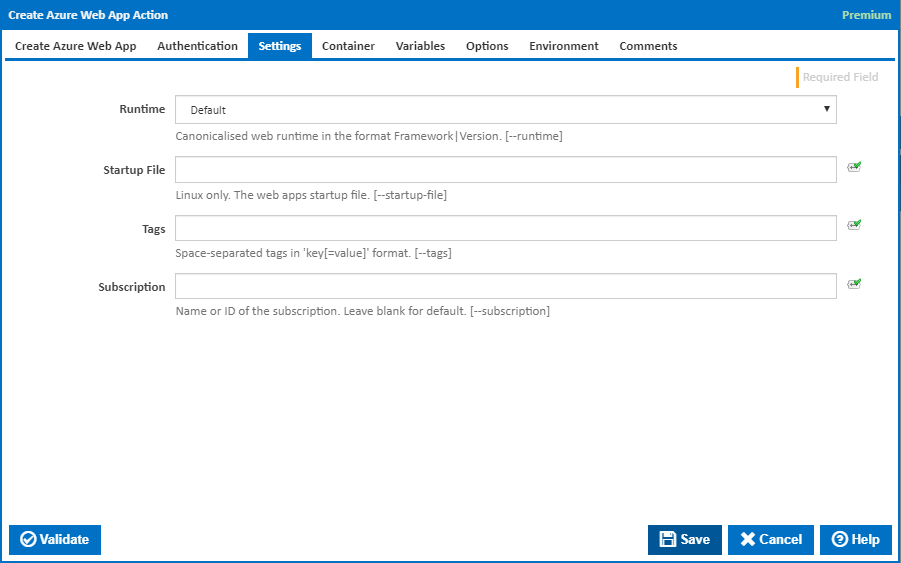
Runtime
Canonicalised web runtime in the format Framework|Version. [–runtime]
Custom runtime
This field is visible when the Runtime is set to 'Custom'.
Specify an alternative runtime. The list of accepted values can be found by running the command line 'az webapp list-runtimes'.
Startup File
Linux only. The web app's startup file. [---startup-file]
Tags
A space-separated list of tags in 'key[=value]' format. Tags let you categorise your Azure resources according to whichever patterns make sense for your organisation's needs. [---tags]
Subscription
The name or ID of the subscription to use. If omitted the default subscription for your environment will be used. [---subscription]
Container
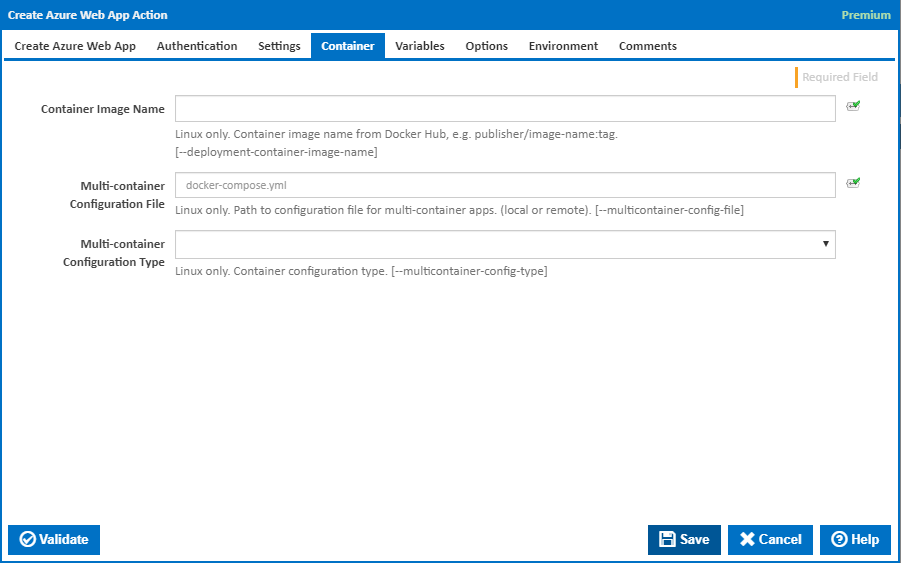
Container Image Name
Linux only. The name of a container image from Docker Hub, e.g. publisher/image-name:tag. [---deployment-container-image-name]
Multi-container Configuration File
Linux only. The path to the configuration file for multi-container apps (local or remote). [---multicontainer-config-file]
Multi-container Configuration Type
Linux only. Container configuration type. [---multicontainer-config-type]
Variables
Location
Select the name of the build variable to set with the location of the new web app.
Resource Group
Select the name of the build variable to set with the resource group of the new web app.
Host Name
Select the name of the build variable to set with the host name of the new web app.
Web App ID
Select the name of the build variable to set with the ID of the new web app.
Outgoing IP Addresses
Select the name of the build variable to set with the outgoing name of the new web app.
Repository Site Name
Select the name of the build variable to set with the repository site name of the new web app.
Options
Log Level
The amount of information detail to display in the build log.
Timeout (in seconds)
How long to wait for the action to finish running before timing out. Leaving this blank (or zero) will default to 86400 seconds (24 hours).
No Response Timeout (in seconds)
How many seconds to wait for the Azure commands to respond with output before timing out. Leave zero to wait until the main timeout.
Treat failure as warning
Tick to continue build on failure marking the action with a warning status.
Ignore warnings
If this is ticked, any warnings logged will not mark the action with a warning status.
Environment
Environment Variables
Multiple environment variables can be defined - one per line. These are set before the command line is run.
Log environment variables
If this is ticked, environment variable values are written to the build log.
Generate system environment variables
Tick this checkbox to set up a list of new environment variables prefixed with 'ContinuaCI.' for all current system expression objects and variables.
Mask sensitive variable values in system environment variables
This checkbox is visible only if the 'Generate system environment variables' checkbox is ticked.
If this is ticked, the values of any variables marked as sensitive will be masked with **** when setting system environment variables. Clear this to expose the values.